Debunking the History and Mystery Behind the Four-Leaf Clover
The four-leaf clover is a rare charm that most people associate with St. Patrick’s Day, but underneath the popularity is a rich and complicated history.
March 24, 2018
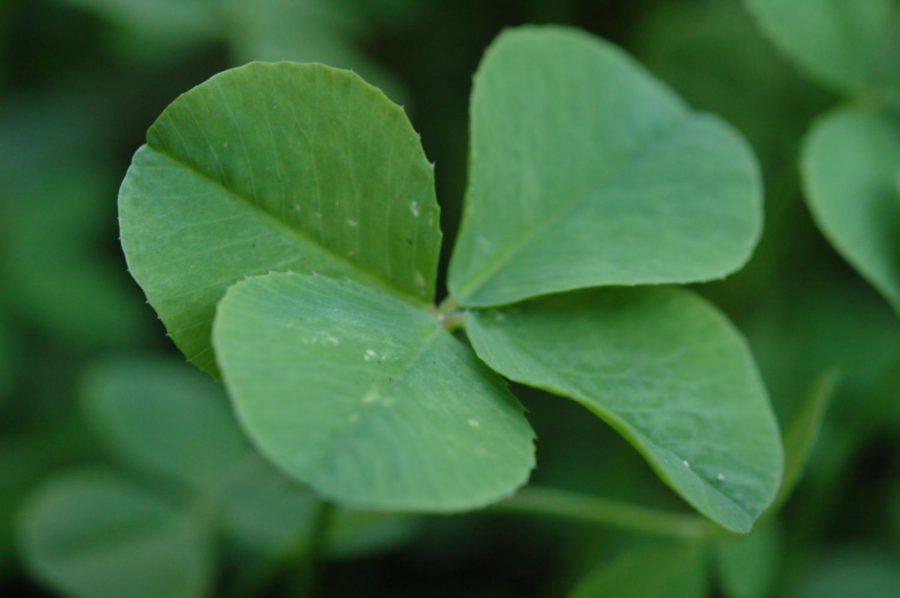
From posters and merchandise to company logos and tattoos, the white clover, more commonly known as the four-leaf clover, is the primary symbol of St. Patrick’s Day. The rare four-leaf form of the white clover is said to bring luck to those who find it.
The story behind three-and-four-leaf clovers originates from Druids, or Celtic priests. They used the three-leaf clover for rituals; Celts believed that the extra fourth leaf allowed carriers to see and ward off demons. Each leaf of the lucky clover represented Faith, Hope, Love and Luck, according to Better Homes & Gardens.
With a probability of one four-leaf clover in 10,000, the iconically lucky fourth leaf is a result of a small but regularly occurring genetic mutation that is strongly affected by environmental circumstances, according to Wired Magazine. Although there are over 300 species of clovers, the white clover, or Trifolium repens, most regularly produces the lucky leaf.
The low probability of a four-leaf clover is due to the species’ confusing genome and genealogy. The white clover holds four chromosomes, twice as many as humans. After attempts to proliferate across the globe in the past, the clover eventually became an allotetraploid, meaning that two of the four complete copies of its genome are from another species, according to everything2.com.
To make this more complicated, as proliferant outbreeders, white clovers breed with any other plant species. So, finding which genes belong to which parent is nearly impossible.
Finding the gene holding the four-leaf distinction was originally difficult to find, but researchers from the University of Georgia discovered that the special gene is caused by two recessive genes, which are genes that are normally not present because they tend to be covered by a more dominant gene of the allele, according to learn.genetics.utah.edu.
Additionally, scientists discovered that the environment plays a larger factor on the white clover leaves. The result of environmental conditions on the genes indicates that warmer weather produces more four-leaf clovers, according to Splice Bio.
Since finding a four-leaf clover is merely a series of dependent events and environmental conditions, the probability of discovering one in an area like Southern California is much more likely than expected.








![Mares demonstrates his lettering while patrolling the campus. “[Calligraphy] wasn’t like baseball or football,” Mares said. “I just liked it. It’s kind of just one of those things that you can relax with.”](https://portolapilot.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/George-Caligraphy-600x450.jpg)